For those who apply for trademarks from overseas to Japan
When you apply directly to Japan, if you do not have a sales office etc,in Japan, you will need to complete the procedures with a local representative in Japan.
When an international application is filed using the Madrid system and Japan is designated as a designated country, a local representative in Japan is required only when the Japan Patent Office (JPO) issues “NOTIFICATION OF PROVISIONAL REFUSAL”.
We will assist you in acquiring trademark rights in Japan as a local representative in Japan.
In the case of trademarks, we believe that we will be able to communicate with you without any problems by exchanging e-mails, but we can also hold video conferences as needed.
Please see here for our video conference.
Although our office is still a small office operated by two patent attorneys, we offer smart services at low cost that are not available at major patent offices.
■Expenses required for filing trademark applications from foreign countries to Japan
■Contact us
Convention on Trademarks to which Japan is a Member
Japan is a member of the following international conventions on trademark registration, filing procedures, etc.
①Paris Convention on the Protection of Industrial Property (enacted in 1883),
②Nice agreement on the international classification of goods and services for the registration of two marks (established in 1957),
③The Marrakesh Agreement to Establish the World Trade Organization Annex I C Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS Agreement, Established in 1994),
④Trademark Law Convention (enacted in 1994),
⑤Madrid Protocol (dated in 1989)
In Japan, a trademark system harmonized with these treaties has been established.
Basic Concept of The Japanese Trademark System
The first-to-file rule
“The first-to-file rule” is a system to prioritize and register those with earlier filing dates.
In Japan, if the same or similar trademark is filed on the same day, it will be decided by “lottery draw”.
Substantive examination system
After the application, the substantive examination of absolute registration requirements such as whether the trademark is not against the public interest or whether it has distinctiveness, and relative registration requirements such as whether or not it conflicts with other person’s prior trademark, and only those that have passed the examination will be registered.
Post-grant opposition system
Japan’s registration opposition system allows any person to seek cancellation within two months from the date of issuance of the trademark gazette issued after registration. The purpose is that the Patent Office examines the propriety of the registration procedure and corrects it if there is a problem with the examination.
One-application multi-classification system
In Japan, a multi-classification system is adopted, and multiple classes can be specified in a single application.
Other
In Japan, the “consent agreement system” and “disclaim system” are not adopted.
Types of trademarks protected
The scope of protection of Japanese trademarks is character trademarks, graphic trademarks, symbolic trademarks, three-dimensional trademarks, combined trademarks, color trademarks, sound trademarks, motion trademarks, positional trademarks, and hologram trademarks.
Other systems include collective trademarks, regional collective trademarks, and defensive marks.
Flow of trademark application (direct application)
Direct applications from overseas are the same as the flow of application procedures in Japan.
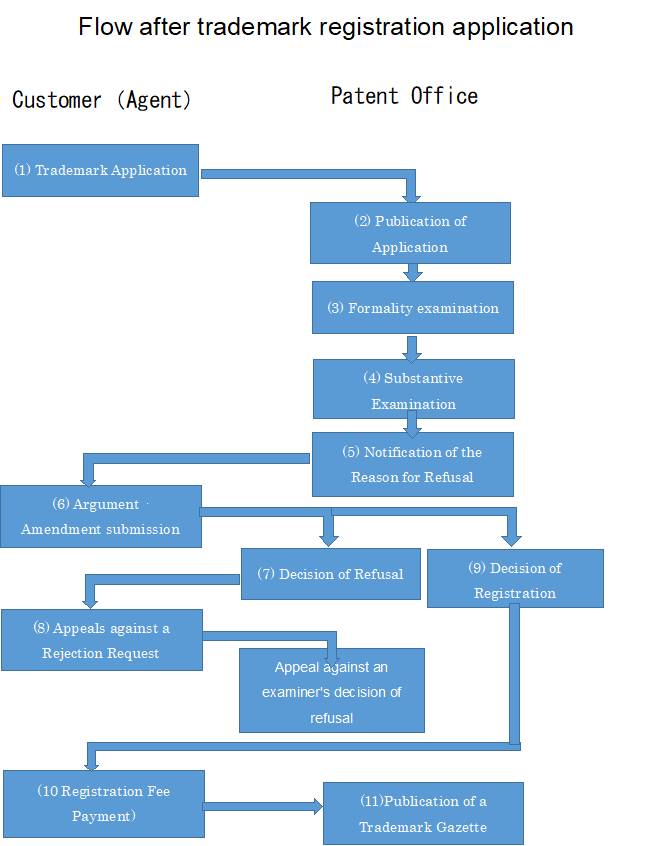
(1)Trademark Application
In the “Trademark Application” that describes the prescribed matters, the trademark and designated goods to be registered with the trademark will be stated ,and submitted to the Commissioner of the Patent Office.
(2)Publication of Application
When a trademark application is filed, the contents of the application will be published in a Publication of Application
(3)Formality Check
It will be examined whether the submitted documents are in accordance with the form or not.
Invitation for Amendment will be issued if the document is not prepared and required items are not listed.
(4)Substantive Examination
Examination is conducted by the Patent Office examiner.
The examiner decides whether the filed trademark should be registered as a trademark.
(5)Notification of the Reason for Refusal
The examiner will notify the applicant of the reason for the rejection if he/she finds a reason for refusal, such as not meeting the registration requirements.
(6)Argument /Amendment submission
The applicant is given the opportunity to submit an argument to the Reason for Refusal and an amendment to correct the content.
(7)Decision of Refusal
If the examiner determines that the reason for refusal can not be resolved even by argument or the amendment, it will make a decision that the refusal should be made.
(8)Appeals against a Rejection Request
If you are not satisfied with the Decision of Refusal, you may request the Patent Office Commissioner to appeal the decision.
An appeal examination against a decision of refusal is performed by a collegial body of three or five appeal examiners.
If you disagree with the outcome of the appeal, you may be able to sue the Intellectual Property High Court.
(9)Decision of Registration
If the examiner finds no reason for refusal as a result of the examination, it will evaluate that it should be registered.
(10)Registration Fee Payment
If you pay the registration fee for the application for which the registration decision has been made, it will be registered in the trademark registry and trademark rights will come into force.
After setting up the trademark right, a trademark registration certificate will be sent to the applicant.
(11)Publication of a Trademark Gazette
The contents of the registered trademark will be published on the trademark gazette.
Application to Japan by madrid system (application for international trademark registration)
Even if you apply for Japan as a designated country using the Madrid system, the flow of the application process is almost the same as in the case of direct application.
The holder of the international registration (agent) may apply for arguments and other procedures with the International Bureau (WIPO).Therefore, you usually do not need a local representative in Japan.
However, if the JPO sends a provisional refusal notification to the WIPO , it will be necessary for the local representative in Japan to respond to the provisional refusal with the JPO, such as the procedure amendment.
The procedure needs to be within the three-month period specified in the provisional refusal notification or notice of reasons for refusal.
You can submit an Argument, etc. to JPO within the period up to 3 months, starting from the next day of the shipping date.
For the period designated in the provisional refusal notification , one request may be made before the expiration of the period and one after the lapse.
- Request for extension of period within the response period of provisional refusal notification: Extension of one month response period is permitted (Fee: 2,100 yen).
- Request for extension of period after response period of provisional refusal notification : Extension of response period of 2 months is permitted (Fee: 4,200 yen)